Where is caffeine found?
This substance is contained in about 60 different types of plants and their products, which are often used as food additives and components for medicines.
For example, mate and guarana extracts, which are included in popular dietary supplements, contain caffeine. Personal experience
Takzdorovo.Ru editor Snezhana Shabanova tells how to get rid of coffee addiction, and the portal’s regular author Maria Skatova shares her personal experience of giving up coffee.
In addition, caffeine is added to colas and energy drinks. Synthesized caffeine is found in medicines, usually for headaches or colds. And yet, the most traditional source of caffeine in the modern person’s diet is coffee and tea.
Beneficial properties of caffeine and its effect on the body
The effect of caffeine on the body was studied by I.P.
Pavlov. Studies have shown that caffeine enhances arousal processes in the cerebral cortex. It also affects the increase in physical activity. Caffeine stimulates performance, while significantly reducing the feeling of fatigue and drowsiness. Using caffeine helps prevent blood clots.
It is noted that coffee lovers are 2 times less likely to suffer from such a terrible diagnosis as a stroke. In addition, coffee increases the body's perception of insulin. This fact suggests that the body is well protected from type 2 diabetes.
So, with fairly moderate consumption, the substance has the following features:
- is a stimulant that reduces the feeling of drowsiness and fatigue;
- improves mood;
- sharpens the functioning of the senses;
- protects against strokes;
- is a stimulator of active blood circulation;
- accelerates metabolism, stimulates fat burning;
- used for vascular spasms;
- used as a natural antidepressant.
- causes an increase in mental and physical activity;
- acts as a trainer for the heart and blood vessels, by increasing the frequency of contraction of the heart muscle.
Interaction with Essential Elements
It is not recommended to consume caffeine and caffeine-containing products immediately after meals. This may negatively affect the absorption of certain vitamins and minerals (magnesium, calcium and sodium).
Caffeine has a mild diuretic effect. If you use caffeine in large quantities, dehydration may occur.
Interacts with analgesics, increasing their bioavailability to the body.
Signs of a lack of caffeine in the body:
- low blood pressure;
- reduced blood cholesterol levels;
- fast fatiguability;
- decreased mental and physical activity;
Signs of excess caffeine in the body:
- hyperactivity and agitation;
- insomnia;
- hypertension;
- tachycardia, cold sweat;
- dry mouth;
- nausea and vomiting;
- frequent urination;
- tinnitus;
- state of anxiety, unjustified anxiety, “tremor”;
- depression, fatigue;
- drowsiness (at very high dosages);
- confusion of consciousness.
Factors affecting caffeine levels in the body
In order for the level of caffeine in the body to be normal, a nutritious diet that includes foods containing it is sufficient. In this case, it is worth paying attention to the individuality of the body: diseases, age, chronic diseases, intolerances and allergies.
Caffeine for beauty and health
Caffeine increases the strength and performance of muscles, promotes their intense contraction. Athletes are allowed to use caffeine before training. Caffeine as a doping is prohibited in competitions.
The benefits of caffeine for creating a strong and beautiful body is the topic of many discussions. There is no definitive answer about the advisability of using it before training.
Caffeine is also an essential component of weight loss creams.
Tatyana Eliseeva chief editor of the Food+ project
Ask a Question
Rating:
8.3
/10
Votes: 5
Usefulness of the material 7.5
Reliability of information 10
Formatting of Article 7.5
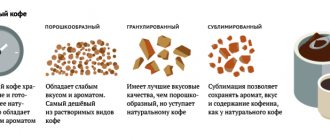
What determines the caffeine content in coffee?
Type of coffee.
Robusta coffee, which is used in instant coffees, contains twice as much caffeine as Arabica coffee, the most common type of coffee bean on the world market.
Thus, a cup of Robusta espresso with a volume of about 170 g contains up to 200 mg of caffeine. A similar cup of Arabica contains about 110 mg. Roasting.
Many people believe that dark roast coffee is stronger because it has a more pronounced taste and aroma.
However, heavily roasted beans contain less caffeine because prolonged processing at high temperatures breaks down the caffeine molecules. Grinding
Different methods of preparing coffee require different degrees of grinding of the coffee beans.
For example, to make Turkish coffee you need to grind the coffee almost into dust, but for a drip coffee maker or press the coffee is ground quite coarsely. Please note that the finer the coffee grind, the more caffeine will be in the finished product, since the substances contained in small particles are more easily washed out with water. Cooking time.
The longer the coffee is brewed, the higher the caffeine level it will contain.
For example, coffee from a press brewed over a long period of time contains more caffeine than coffee brewed instantly using ristretto steam.
Is there a caffeine overdose?
Since caffeine is a psychostimulant, it can cause unwanted complications if consumed in excess. First of all, in case of overdose, the nervous, cardiovascular and digestive systems are affected. Severe intoxication can lead to confusion and epileptic seizures. But most often, an excess of the substance is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- tremor of the limbs;
- tachycardia;
- anxiety;
- increased blood pressure levels;
- headache.
First aid is to provide oxygen access by opening a window. It is equally important to immediately call an ambulance. To remove excess alkaloid from the body, you should take adsorbent drugs. These include Enterosgel and activated carbon. You should also drink as much fluid as possible.
Advice! To prevent dehydration due to poisoning, you can take Regidron.
What determines the caffeine content in tea?
There is no caffeine-free tea.
Coffee can be completely freed from this substance.
However, any type of real tea, both black and green, will contain caffeine. Type of tea.
Varieties of teas vary in caffeine content. Black teas contain the most of this substance: a 200 g cup contains from 60 to 85 mg of caffeine. White teas confidently occupy second place: a cup of the same volume contains up to 75 mg of this substance. A cup of regular green tea contains 30 to 60 mg of caffeine.
Which product has the most caffeine?
Many products contain caffeine, but coffee occupies a leading position in its content. It contains many antioxidant substances that protect the human body from the harmful effects of free radicals and trigger metabolic processes. Its presence in the diet in moderation ensures that energy reserves are maintained at the required level.
The tonic substance has the property of activating the urinary system
Type of tea.
Cheap teas made from ground or crushed leaves packaged in tea bags produce a drink that contains more caffeine than tea made from whole leaves. In addition, tea made from the top young leaves and tea buds is also richer in caffeine than teas made from the “old” leaves. By the way, rolled leaves release caffeine more slowly than regular leaves. Brewing temperature.
The caffeine content in a cup of finished tea largely depends not on the type of tea, but on the method of brewing it.
For example, if you brew green tea with water that has cooled to 70-80 degrees, the caffeine content in the drink will be lower than in one brewed with boiling water, since the infusion (the amount of extractive substances released into the water) will not be too strong. A similar rule applies to black tea. Iced teas.
Sweet bottled teas also contain caffeine. It is formed when brewing tea or added additionally. On average, such drinks contain from seven to 15 mg of caffeine per 100 g.
Coffee and white teeth
Frequent consumption of coffee and coffee drinks makes tooth enamel yellow. Find out how to keep your teeth white if you can't imagine your day without a cup of coffee.
Impact on the body
In small quantities, the substance has a stimulating effect on the body. The cardiovascular system reacts first: the heart rate increases and blood pressure rises. Therefore, the morning of hypotensive patients begins with a cup of coffee, and this drink is contraindicated for hypertensive patients. Then a surge of dopamine helps improve your mood. Following the heart, the central nervous system reacts to the substance: brain activity improves and physical performance increases.
- Don't miss: How coffee affects the human body
The nature of the effect on the body largely depends on the individual characteristics of the human nervous organization. Interactions with some medications are possible, so you may have to give up coffee and tea during treatment.
Caffeine enters the bloodstream 40-50 minutes after consumption. The effect of caffeine is 3-6 hours, so people sensitive to it should avoid invigorating drinks in the afternoon. Caffeine is completely eliminated from the body 14 hours after consumption.
In women, the elimination process is a little slower, and in smokers it is faster.
With regular, long-term use, a weak attachment to coffee or tea arises: without a cup of your favorite drink, it can be difficult to wake up and gather strength. From a medical point of view, caffeine is a drug, but due to its low concentration in products, there is no ban on drinking tea and coffee. Energy drinks with a substance concentration of more than 150 mg/l must contain a mention of possible harm to health and prohibition for children and pregnant women.
How much caffeine is in sweets and drinks?
- Various types of cola contain from 15 to 20 mg of caffeine per 100 g.
- A standard can of energy drink (230g) delivers between 70 and 300mg of caffeine. When purchasing this drink, be sure to study the composition - the manufacturer must indicate the caffeine content in their product.
- A 200g cup of cocoa contains about 20mg of caffeine.
- A piece of dark chocolate weighing about 30 g - 20 mg of caffeine.
- A piece of milk chocolate weighing about 20 g contains six mg of caffeine.
- White chocolate does not contain caffeine.
Products with the highest caffeine content
Certain caffeine-containing products have been identified. The list of those that contain the most of this alkaloid is relatively small:
- Chocolate. After consuming this product, a person feels a surge of strength. This is due to the presence of an invigorating component in chocolate. One hundred grams of sweet delicacy (black or milk) contains about 30 mg. There is no alkaloid in white chocolate.
- Chocolate ice-cream. 200 g of this product contains about 80 mg of natural stimulant.
- Cocoa. This product has been known to everyone since childhood. It is noted that 200 ml of prepared hot cocoa contains about 30 mg of the invigorating alkaloid. In 100 g of dry powder the concentration reaches 230 mg.
- Energy bars. They contain up to 75 mg of an invigorating substance.
How much water do you need?
While it's generally recommended to consume at least 8 cups (64 ounces or 1.9 liters) of water per day, there is no universal recommendation for how much water you should drink per day. Water needs depend on many factors, including where you live, your activity level, diet, body size and age.
As a general guide, the National Academy of Medicine has developed the following recommendation for daily water intake—from both food and beverages—for adults aged 19 years and older:
women: 91 ounces (2.7 liters) per day
men: 125 ounces (3.7 liters) per day.
These recommendations are based on the average intake of generally healthy people with sufficient water. Food accounts for approximately 20% of the recommended total water intake, with the remaining 80% coming from drinks such as tea, coffee, water, juice and soda.
Summary: Your water needs depend on where you live, how active you are, what you eat and drink, your body size and your age.
What is caffeine
Let's start with the question of where caffeine is found. This alkaloid is found in tea leaves (up to 2%), coffee seeds (up to 2%), and cola nuts (2-2.5%). It is found in the leaves and shoots of mate, guarana climbing vine, and cola seeds.
There is also an artificial analogue of this substance with the same formula: C8H10N4O2. Caffeine in Latin sounds like Coffeinum, and its name according to the international classification is 1,3,7-trimethylxanthine. Not only the name is complex, but also the structural formula of the substance:
Its physical properties:
- Appearance: white, needle-shaped crystals or powder;
- bitter taste;
- no odor;
- good solubility in hot water;
- poor solubility in alcohols;
- neutral reaction (does not have acidic and (or) alkaline properties).
Initially, people used only the pharmacological action of the substance. Caffeine is a powerful central nervous system stimulant, which helped recover from operations or illnesses, increased the overall tone of the body, extracting additional energy from it.
The first coffee shops appeared in Europe 400 years ago. In England, in London, a coffee shop was opened in 1652. It is noteworthy that women were not allowed into it: drinking coffee was considered a male privilege. From this date, coffee shops gradually began to open and coffee moved from “overseas exotic” to the category of everyday drinks.
We owe the appearance of the world-famous drink Coca-Cola to the cola nut. The drink was created by pharmacist John Pemberton, and it was intended for chronic fatigue, toothache and depression. Moreover, they bought it up extremely reluctantly. Then carbonated water was added to the composition and diluted with sugar, after which the Coca-Cola drink became popular.
How caffeine gets into the blood
Thanks to its lipophilic properties or ability to dissolve in fats, coffeinum easily penetrates the body, having a stimulating effect on it. Lipids are part of cell membranes, creating a barrier to “foreign invasion.” But since the alkaloid easily dissolves in them, it:
- It quickly passes through the intestinal walls, entering the bloodstream. At the same time, cell membranes are not a hindrance for it.
- Liquid products containing caffeine are absorbed faster, while solid products are absorbed a little slower.
- After an hour, the maximum concentration of caffeine in the blood is reached.
- Up to 80% of trimethylxanthine settles in the liver, where it breaks down into theobromine, paraxanthine and theophylline, which are excreted from the body after 3-7 hours.
- Caffeine circulates through the blood for about 4-6 hours (half-life), which depends on the action of metabolism.
In 1918, the German organic chemist Ferdinand Runge discovered caffeine, and by the end of the century, Hermann Fischer synthesized it artificially, having carefully studied the structure of the substance. In 1902, he received the Nobel Prize for the synthesis of caffeine.
Metabolism
Let's look at the mechanism of action of caffeine step by step. Trimethylxanthine molecules in the body:
- attach to adenosine receptors, which signal the brain about fatigue;
- thanks to the neutralization of adenosine, the state of vigor is prolonged;
- at the same time, there is an increase in the level of dopamine and serotonin, which are “responsible” for a good mood;
- The adrenal glands release the hormones adrenaline and norepinephrine, which causes blood pressure to rise in the body and heart rate to increase.
The action of coffeenum is related to the time of day. In the morning, its stimulating effect is most pronounced, since at this time other internal stimulants of the body are activated. And caffeine has synergism, enhancing the effect of substances that excite the central nervous system. In the morning, the stimulant caffeine is useful: it increases productivity and mood, which is important before starting the working day. The duration of action of caffeine depends on many factors:
- dose used;
- age;
- weight;
- health conditions;
- food preferences;
- metabolic rate;
- individual characteristics.
To stimulate the body, coffeinum is most often taken with drinks, which enhances the functioning of the central nervous system within 20-45 minutes. If the alkaloid is used in the form of capsules or tablets, the effect occurs more slowly: after an hour or more.
The alkaloid in a cup of coffee is a psychostimulant. It is not prohibited anywhere and for this reason it is actively consumed by up to 80% of the world's population. Caffeine is a drug that sooner or later becomes addictive. Mental dependence syndrome is known as “caffeineism,” when after quitting coffee, the emotional and physical state declines.