The answer to the question of how much alcohol leaves the body primarily depends on the strength of the drink consumed and the amount drunk. Body features and the general health of a person are of great importance. But an improvement in well-being, the disappearance of euphoria and other symptoms of intoxication does not mean that the body has completely cleared itself of ethyl alcohol. Sometimes this takes more than a day.
Features of ethanol metabolism
The absorption of ethyl alcohol begins in the oral cavity and esophagus, a fifth of what is drunk is absorbed in the stomach, the remaining 80% in the duodenum. Ethanol from low-alcohol drinks, especially carbonated drinks, enters the blood faster. Strong alcohol reduces the permeability of the cellular epithelium, which slows down its absorption. Alcohol spreads through tissues and other liquid media, is partially excreted unchanged through the sweat glands, lungs (with exhaled air), kidneys, and is found in breast milk and feces. Alcohol penetrates into the brain tissue and remains there even in the elimination phase (removal from the body); high concentrations are also detected in the prostate gland, testicles and sperm; in pregnant women, it quickly enters the fetal bloodstream. Most of the ethyl alcohol is metabolized.
This process occurs primarily in the liver by:
Oxidation inside hepatocytes under the influence of alcohol dehydrogenases to acetaldehyde. This is one of the main biotransformation pathways, thus breaking down up to 80% of alcohol.- Oxidation using the microsomal ethanol-oxidizing system of the liver with the participation of cytochrome P-450.
- Oxidation in tissues under the influence of catalase, oxidases and peroxidases. According to this principle, about 10-15% of ethanol is metabolized, but with pathological dependence this figure increases.
The final stage of alcohol biotransformation is the breakdown of acetaldehyde to acetate with the participation of aldehyde dehydrogenase to water and carbon dioxide.
Why does caffeine invigorate you?
Caffeine is a mild central nervous system stimulant.
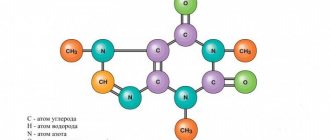
In moderate quantities, it has a positive effect on the brain and cognitive abilities: improves memory, enhances attention and helps concentrate. The structure of the caffeine molecule resembles the structure of adenosine, a neurotransmitter that regulates the transmission of nerve impulses. For this reason, caffeine can bind to adenosine receptors on brain cells, stimulating activity.
The binding of adenosine to receptors promotes relaxation, depresses the nervous system and causes drowsiness. But this does not happen if all the receptors are occupied by caffeine. As a result, a person feels a temporary surge of vigor and activity.
What determines the time it takes to eliminate alcohol?
Amount of alcohol consumed. In a healthy person with average body weight, the rate of breakdown of pure alcohol is 10 g per hour. Accordingly, the higher the dose of ethanol, the longer the metabolic processes will continue.- Weight. In obese people, the period of time it takes for alcohol to be eliminated from the body is almost half that of a person with a normal physique.
- Floor. Due to the lower levels of alcohol dehydrogenase in women, the biotransformation of ethanol occurs approximately 20% slower.
- Presence of liver pathologies. Damage to hepatocytes, the formation of areas of necrosis, fibrosis increases the time of cleansing organs and tissues from ethanol.
- The amount of food taken at the same time as drinking. Eating a large snack slows down the absorption of alcohol.
Diabetes and coffee
I have a very complicated relationship with coffee. I went through a full cycle of relationship with him - from falling madly in love, developing a real coffee addiction with 10 cups a day to the present moment when I consciously drink it very rarely, but with great joy and tender love.
I think that this is exactly the history of our relationship with coffee because it is a complex drink. And from the point of view of taste, and from the point of view of composition, and even from the point of view of writing texts about it. For several months I could not pull myself together and collect all the scattered material from thousands of sources together, I really suffered, and printed articles about coffee flew with me to Yerevan, and to Shiraz, and to Barcelona, and to Tallinn.
Meanwhile, coffee has a complex relationship with diabetes. The difficulty in studying this issue is due to the amount of information available and the fact that many researchers have found contradictory results. But let's take it in order:
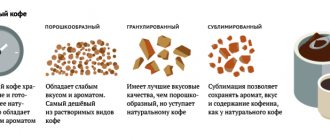
- Coffee is the main source of caffeine consumed worldwide among adults.
- The biological effect of coffee as a drink is not limited to the action of caffeine alone; the drink contains hundreds of biologically active substances - probably one of them made me coffee dependent.
- Here are the results of the most interesting, in my opinion, studies on the relationship between coffee consumption and your health, conducted in the last five years:
- Caffeine may be used to better recognize hypoglycemia during exercise in people with type 1 diabetes. But, on the other hand, it can also increase the risk of developing hypoglycemia the morning after exercise;
- In healthy volunteers who agreed to take caffeine as part of the experiment, the insulin sensitivity coefficient changed. People with type 1 diabetes mellitus did not participate in such studies, however, the fact that this phenomenon was described requires, in my opinion, care when calculating insulin doses;
- Drinking more than three cups of coffee per day is associated with a lower risk of stroke in people without diabetes. In the presence of diabetes mellitus, such a connection was not identified;
- Caffeine may enhance the effect of glucose-lowering drugs from the group of glucosouric substances. These are medications that lower blood sugar levels by excreting it in the urine;
- Regular consumption of 3-4 cups of coffee per day significantly reduces the risk of developing type 2 diabetes;
- The risk of developing type 2 diabetes mellitus is reduced by drinking both regular and decaffeinated coffee;
- Coffee is contraindicated for people with high blood pressure, as it increases the risk of developing cardiovascular complications in people with hypertension;
- Several studies have demonstrated the beneficial effects of coffee consumption on liver function, even in the presence of, imagine, cirrhosis;
- The potentially positive effect of coffee also lies in protecting against certain neurological diseases, improving the course of bronchial asthma, and reducing the risk of developing certain gastrointestinal diseases;
- Potential risks of drinking coffee (mainly due to the caffeine content) include increased anxiety, insomnia, tremors, palpitations, and decreased bone mass and therefore a potential increased risk of fractures.
In summary, I would say this: enjoy your coffee, if you like it, enjoy every drop of it, but do not forget that this drink can affect your glucose levels or change the risk of developing certain diseases - both in one and the other. the other side. Take care of yourself!
Approximate period of alcohol elimination
The approximate time frame for how many hours alcohol is removed from the body (in the absence of pathologies of the liver, digestive tract, metabolic disorders) is indicated in the table.
| Type of alcoholic beverage and ethanol content | Weight | ||
| 60-70 kg | 80-90 kg | 100 kg or more | |
| Beer and other low-alcohol cocktails (4-6%) | 35-50 min. | 25-40 min. | 20-30 min. |
| Champagne, wines (11-18%) | 1.5-2.5 hours | 1-2 hours | 1-1.5 hours |
| Liqueurs and tinctures (24-30%) | 3-4 hours | 2-3.5 hours | 2-2.5 hours |
| Vodka, cognac, whiskey, tequila and other strong alcohol (40% or more) | From 5 hours | From 4 hours | From 3.5 hours |
Data on how much alcohol is excreted from the body is given per 0.1 liter of drink.
Sugar
Finally, about the main drug of humanity. The sugar you add to your coffee is made up of glucose and fructose molecules. Glucose is a universal form of energy that powers the entire body, and especially the brain. An adult needs about 200 grams of glucose daily, which he gets not only from sugar, but also from other carbohydrates. The peculiarity of sugar is that it breaks down into glucose almost instantly and causes a quick surge of energy.
The body's job is to maintain stable glucose levels in the brain. When there is too little of it, our mood drops, attention, memory and ability to perceive new information deteriorate. Participants in experiments who were given a glucose drink after several hours of fasting performed better on verbal and spatial memory tasks. A sharp decrease in glucose levels, even in people without epilepsy, can lead to seizures.
In a stressful situation and with a high mental load, the brain requires more glucose than usual. People who received a dose of glucose before taking memory tests performed better on the tasks. But the data here is ambiguous. In another experiment, participants who were given glucose rather than slower sugars (fructose or sucrolose) performed the worst on tasks.
It’s not for nothing that they scare us with horror stories about sugar: too much glucose consumption does not lead to anything good. This is especially obvious in the case of diabetes, a disease in which the body's glucose levels are constantly elevated. Diabetes causes impairment of memory, visual perception, attention and productivity, and also doubles the risk of Alzheimer's disease.
More recently, scientists have found that excessive sugar consumption, even in people without diabetes, gradually deteriorates memory and other thinking abilities.
Apparently, high glucose levels cause premature aging of nerve cells. A diet with a high glycemic index increases the risk of cognitive impairment by 80% and is associated with decreased IQ in young adulthood. Rats fed fructose became worse at completing mazes after just 6 weeks. High sugar consumption can cause metabolic syndrome - a disorder of carbohydrate metabolism that causes obesity, increased fatigue, apathy and frequent headaches.
Is it possible to speed up the metabolism of alcohol?
To reduce the time it takes for the body to cleanse itself of alcohol, it is recommended to use the following methods:
Take a contrast shower. This water procedure stimulates blood circulation and improves oxygen supply to tissues.- Drink more water, as alcohol abuse is accompanied by dehydration.
- Drink Regidron or other similar drugs (can be replaced with homemade brine) to restore electrolyte deficiency.
- Eat chicken broth soup, this helps normalize the digestive tract.
- Take a walk in the fresh air.
- Take Aspirin to relieve pain.
However, these methods are suitable after one-time alcohol abuse. If you are on a long-term binge, it is better to entrust detoxification to professionals. Depending on how many days a person drinks, cleansing the body is carried out either at home or in a hospital.
For this use:
saline and nutrient solutions;- multivitamin complexes;
- drugs to prevent hypoxia and the consequences of oxygen starvation of tissues;
- medications to protect liver cells from the toxic effects of ethanol and its metabolic products;
- medications to normalize blood pressure and heart rate;
- diuretics to stimulate kidney function and eliminate alcohol biotransformation products;
- sedatives to relieve withdrawal symptoms.
Other medications are used according to indications.
Such measures significantly reduce the time it takes for ethanol to be eliminated from the body. Often, detox therapy serves as the first stage of treatment for persistent alcohol addiction. Subsequently, psychotherapy and physiotherapy are indicated, and many coding methods are offered. Many private drug treatment clinics operate rehabilitation centers where the results of treatment can be permanently consolidated.
Need some advice?
OR CALL A DOCTOR
CALL!
+7
Symptoms of caffeine overdose
When intoxicated, the gastrointestinal tract, nervous and cardiovascular systems are primarily affected.
Signs of caffeine overdose:
- state of anxiety and panic;
- headache;
- increased sensitivity;
- tremor of the limbs,
- increased blood pressure;
- tachycardia.
Dangerous concentrations of caffeine are characterized by pain in the stomach and intestines, nausea, vomiting, muscle spasms, motor restlessness, confusion, ringing in the ears, and breathing problems. Severe intoxication can cause loss of orientation and an epileptic seizure, accompanied by seizures and convulsions. When the first signs of poisoning appear, you must immediately begin to cleanse the body.